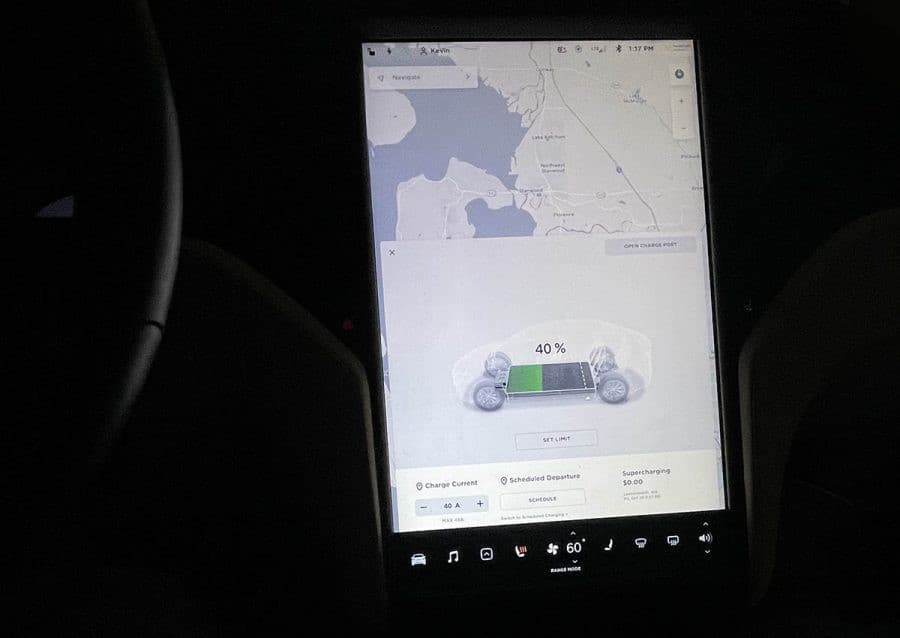
Tesla has long been known as the best of the best in electric car design. Their cars are stylish and come equipped with every innovation Tesla can pack into them. However, how do Tesla’s electric vehicles stack up from a practical standpoint? Does the charging length and capacity of a Tesla speak to their stellar reputation?
The length of time it takes to charge a Tesla depends on three factors: the charging system, the battery capacity, and the onboard charger. While knowing the time needed for a charge is essential for planning purposes, you cannot overcharge your Tesla due to the car’s monitoring features. It is typically recommended to charge your Tesla between 50-80% charge, depending on your daily driving needs. Charging to 100% frequently can prematurely degrade your battery.
With three factors impacting charging time, it is quite the math problem to figure out how long it takes to charge your Tesla, and although you cannot overcharge your Tesla, you can reduce the battery life with certain charging practices. Do not get stressed yet! We have researched for you. Keep reading for everything you need to know about charging a Tesla!
The Basics of Charging a Tesla
Before we can start looking at the specifics of charging a Tesla, it will be helpful to cover exactly what happens when you charge an electric vehicle.
When we fuel a gasoline-powered vehicle, we think of distance in miles per gallon. This many gallons will get me this far. Electric vehicle’s fuel capacity is in kilowatts per hour (kWh). The car stores so many kWh in its battery, which you use up as you drive. The distance you can go on 1 kWh depends on the car, your driving, and the terrain.
When you charge an electric vehicle, the charger ability is measured in kilowatts of energy, but the battery storage within the car is in kilowatts per hour, so what is happening? Kilowatts is the speed of energy flow, while kilowatt-hours is the amount of energy stored.
A charging unit has a kilowatt rating, which tells you how fast it can transfer kW to your Tesla, while the Tesla itself has a kilowatt per hour storage, which tells you how much energy your Tesla can hold. Thus charging time is determined by how fast the energy is flowing (kW) and how energy your Tesla can hold (kWh).
Sounds simple enough, right? Higher kW means faster-charging speed, and higher kWh means more time needed to fill the battery and a longer-lasting charge. Now that we understand the basic principle let’s look at the specifics that change charge time.
The Onboard Charger
Most electrical outlets from which we get electricity use AC (alternating current). However, batteries, such as the one in your Tesla, use DC (direct current). This means that your Tesla must have a system to convert the AC into DC that can be stored in the battery. This system is called the onboard charger.
The onboard charger has its own restrictions on how fast it can convert energy. Teslas come with either an 11.5 kW (48 amp) or a 7.7kW (32 amp) onboard charger. If you plug your Tesla into an AC outlet, then, no matter what the outlet’s power, it cannot charge at a faster rate than the onboard charger will allow, 11.5kW or 7.7kW depending on the Tesla.
It can, however, charge at a slower rate. The amp ratings on the onboard charger represent the max the system can handle. The kW ratings given are based on charging your Tesla with a 240V AC outlet, which is the highest AC to which you would have access.
The math behind this is quite simple. kW is the product of amps and voltage divided by 1000. If you plug your Tesla into a 240V outlet and your Tesla’s onboard charger has an amperage of 32, then your kW would be 240 x 32/1000, which equals 7.68kW, which Tesla has rounded to 7.7kW.
To ensure your Tesla is reaching its kW rating, you will need to ensure that the onboard charger is pulling the maximum amount of amps it can. For a 48 amp onboard charger, Tesla thus recommends a 60 amp circuit breaker, and for a 32 amp onboard charger a 48 amp circuit breaker.
Levels of EV Chargers
The first, and also most important, thing to consider when figuring out how long you need to charge your Tesla is the charging system. The charging system determines your kilowatts, which is to say that it determines the speed at which energy is transferred to your Tesla.
The more kilowatts a charging system uses, the faster your Tesla will charge. There are 3 levels of electric vehicle charging systems. These levels are divided by their voltage ratings.
Level 1
Level 1 EV charging is charging your vehicle with a standard 120V outlet, which is what a basic electrical outlet around your house is. Level 1 EV charging (120V) is the slowest form of charging. It generally only provides 2 to 4 miles of driving for every hour of charge.
A 120V outlet at your house is AC. Thus the onboard charger will come into play to convert this to DC. If your Tesla has the 11.5 kW 48 amp onboard charger, then plugging it into a 120V outlet only allows a charge of around 5.8 kW. At that rate filling, a 100 kWh battery will take at least 17 hours.
Except there is a problem. 48 amps are how much your onboard charger can handle, but that does not necessarily mean that is what your outlet is giving. A 120V outlet probably only has 15 amps. Knowing that your Tesla’s charging rate decrease to 1.8kW. Filling a 100kWh battery will take around 55 hours.
These numbers come from an ideal setting in which things such as temperature and efficiency do not also reduce charging time. In addition, Teslas charge more slowly as they reach capacity in order to protect the battery. The result is that using a Level 1 charging system to charge your Tesla will take several days for a full charge.
Why Level 1?
If Level 1 takes so long, why does anyone use it? Firstly, Level 1 does not require any special equipment other than an adapter which allows you to plug your vehicle into a normal outlet, and since all Tesla’s come with a free adapter, Level 1 is free charging.
For many people, the long charging time is not a real problem. If you can leave your Tesla plugged in for 10 hours every night then you will likely be able to drive 25 to 40 miles the next day. Many daily commutes are well under this amount.
For those who do not have extra long commutes and who keep their Tesla plugged in whenever they are home (as Tesla recommends you do), Level 1 charging can be a functional option.
Level 2
Level 2 charging involves using a 240V outlet instead of a 120 volt. This will require a different type of adapter. Although they are not as commonly found, homes typically have 240V outlets for larger machines such as the washing machine. Most of the time, however, level 2 charging requires particular equipment.
A Level 2 charger will double your charging rate and more. A 240V charging system often pulls far more amps, which means it is typically able to handle at least 32 amps. A 240V with 32 amps will create a rate of 7.7kW. With this, you can charge a Tesla with a 100kWh battery in around 13 hours.
Why Level 2?
Level 2 provides far faster charging, which for most people is a benefit that far outweighs the extra cost, and it will cost you. Although there are some 240V outlets in your house, your appliances are probably already hooked up to them so you will need to arrange to have an outlet put in and get the correct adapter for charging your car.
Level 3
Level 3 is the fastest charging available, but it is not something you can use in your home. The amount of electricity needed to run a Level 3 charger is not something any homeowner has access to. Level 3 chargers use over 400V and are found in the form of public charging stations.
Level 3 chargers will charge an electric vehicle at an incredible rate. They can charge a car in 30 minutes. The secret behind this supercharging is not just the powerful voltage, but also the current. Level 3 chargers provide DC, which completely bypasses the limitations of the onboard charger.
Level 3 chargers for electric cars are somewhat like gas pumps for traditional vehicles. You have to pay to use them, and they are often strategically placed as stations. If you have a Tesla, the Level 3 chargers available to you are called Tesla Superchargers.
Why Level 3?
Level 3 chargers will charge your car incredibly fast, but you will have to locate and pay for this service. Because of this most people use a home charging system for their daily charging needs and save public chargers for trips.
Even the best electric car can only travel about 350 miles on a full charge. If you are taking a road trip, public charging stations become a must. Thus, if you own a Tesla you will likely be making use of the Tesla Superchargers at some point.
Tesla’s Recommendations
Tesla does not leave its customers in the dark when it comes to charging their vehicles. Tesla has four different options for charging your Tesla that they recommend. For the least hassle, you can use one of Tesla’s products to charge your Tesla.
Mobile Adapter
The mobile adapter comes with every Tesla car. This allows you to charge your Tesla using any standard 120V outlet. This is Level 1 charging and thus will only charge your Tesla at about 4 miles of ranger per hour.
Because of the slow charging rate, Tesla recommends using a better charging option in your home, while keeping the mobile adapter in your car for emergency use.
Wall Connector
This is the product that Tesla recommends for charging your Tesla at home. The Wall Connector is a Level 2 charging solution that Tesla sells for your home. It costs around $500.
The Wall Connector’s effectiveness will be determined by the circuit breaker it uses. For the most efficient charging, you need to ensure that your circuit breaker matches your car’s onboard charger. For a 48 amp onboard charger, you need a 60 amp circuit breaker, and for a 32 amp onboard charger, you need a 40 amp circuit breaker.
A wall connector can give your Tesla up between 25 and 44 miles of range per hour depending on the model of Tesla and the circuit breaker. No matter what this is far more than you can get from just the mobile adapter.
Supercharger
The third charging option specifically designed by Tesla is their superchargers, which are public charging stations. The Tesla Superchargers can charge your Tesla in 30 minutes.
If you plan to take your Tesla on a road trip, you will need to make use of Superchargers. Luckily your Tesla also comes equipped with a GPS that will plan your route including supercharging stations.
Destination Chargers
Destination chargers are also meant to benefit Tesla drivers on a road trip. Destination chargers are Tesla charging stations set up at destinations such as restaurants and hotels. These are not superchargers, but they will allow you to charge your Tesla overnight at a hotel or for several hours while enjoying a nice meal.
Battery Capacity
How much energy your battery can hold will naturally have a large impact on how long it takes to charge. However, more battery storage also allows you to go farther on a single charge, which for most people means they want the largest battery storage they can get.
Tesla’s Model 3 and Model X currently have the largest battery capacity in the electric car market at 100 kWh, giving these cars the longest range in the electric car market as well.
Longer range is great, but what does this larger battery capacity do to charging time? Let’s look at an example. Let us say that both cars have an onboard charger that can handle 48 amps, and they are both hooked up to a Level 2 charger on a 60 amp circuit breaker. In this case, the only difference will be that one car has a 75kWh battery and the other is a 100kWh battery.
In this case, the 75kWh battery will take at least 6.5 hours to charge, and the 100kWh battery will need at least 8.5 hours. Remember that these are low numbers, which represent an ideal situation. It seems then that the 100kWh battery takes around 30% longer to charge fully due to its extra capacity.
The example we just did however has the batteries charging from empty, which you should rarely ever do. If you wish to charge both a 75kWh battery and a 100kWh battery for 40% of their capacity then the difference in charging times would be a little less than an hour.
Thus, the increased range is well worth the extra charging time. If you keep your Tesla plugged in regularly you probably won’t even notice the extra time a 100kWh battery needs.
Application to Tesla’s Different Models
We have discussed in detail the various factors that affect the time needed to charge a Tesla. However, this can be a lot of information to wrap your head around. For simplicity’s sake, we have created a chart showing a comparison between the charging time for different Tesla models using different EV charger levels.
Please remember that the numbers we use in this chart represent an ideal scenario, which rarely happens. You should treat these calculations as minimum charging times.
| Tesla Model | Battery Capacity | Onboard Charger | Level 1 Charging (120 volts, 15 amps) | Level 2 Charging(240V, 60 amps) | Level 3 Charging(Tesla Supercharger) |
| Model SLong Range Plus | 100 kWh | 11.5 kW48 amp | 56 hours | 8.7 hours | ~ 1 hour |
| Model 3Long Range | 75kWh | 11.5 kW48 amp | 42 hours | 6.5 hours | ~ 40 minutes |
| Model 3Standard Range Plus | 55kWh | 7.7kW32 amp | 30.5 hours | 7 hours | ~ 30 minutes |
| Model XLong Range Plus | 100kWh | 11.5 kW48 amp | 56 hours | 8.7 hours | ~ 1 hour |
| Model YLong Range | 75kWh | 11.5 kW48 amp | 42 hours | 6.5 hours | ~ 40 minutes |
This chart provides a basic breakdown of the charging times for Tesla’s top models. These are not all the models that Tesla currently has. Many models have versions with smaller battery capacity, so be sure to check the battery capacity and onboard charger specs for whatever particular model you have.
How Does a Tesla Compare to Other Brands?
If you want to compare the charging times of a Tesla to other electric cars, there are two important things to remember: hybrids and battery capacity.
Hybrid cars, which use both electrical power and gas, often take far less time to charge. However, this is not because they are more efficient at charging but because their battery capacity is much smaller. Hybrid cars do not rely solely on electricity, so they do not need to store nearly as much as an all-electric car, like a Tesla, does.
Tesla electric cars are known for their impressive battery capacities. Many other electric car brands only have 40kWh or 60kWh batteries. This means that a Tesla may take longer to charge fully, but that charge will also give you a much longer range.
How Should I Charge My Tesla?
Now that you know how long it takes to charge your Tesla, you are likely wondering how long you should charge your Tesla. Will overcharging your Tesla damage its battery? Do you need to set an alarm in the middle of the night, so you remember to unplug your car? Do you need to let your Tesla’s battery die all the way down before charging?
Here is what you need to know about best practices when charging your Tesla.
You Can’t Overcharge A Tesla
You cannot overcharge a Tesla. Overcharging a battery can damage the battery and shorten its life, so most rechargeable batteries nowadays come with a monitoring system that will cease charging once the battery is full. In this sense then it is impossible to overcharge your Tesla.
Setting Your Tesla’s Charging Limit
Tesla vehicles take monitoring this charging limit one step further. Using your Tesla app you can set at what percent battery capacity you want your Tesla to cease charging.
To make your battery last, it is best to select a maximum of 90% as the point at which your Tesla stops charging. 80% or 85% would be even better. If your Tesla charges to 100% every time, it will be less energy efficient when driving, which shortens the overall battery life. Even Elon Musk advises customers not to charge their Tesla to 100%.
This ability to set a charging limit is something that places a Tesla above other electric car brands. Charging an electric car past 100% is bad for the battery and can reduce its life. Setting the limit below 100% is a valuable tool that will make your car’s battery perform well for a longer time.
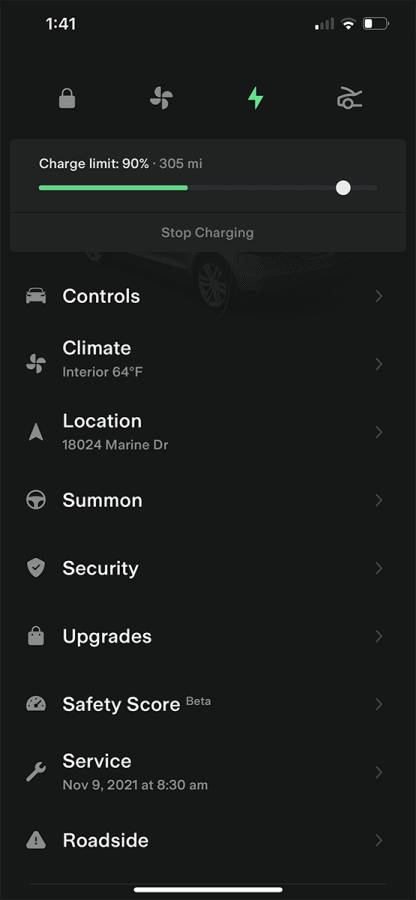
Should I Keep My Tesla Plugged In, or Should I Only Charge When the Battery is Low?
Because the battery will cease charging when it reaches the designated capacity, there is little harm in keeping your Tesla plugged in at all times. In fact, there may actually be some benefits to this approach.
Tesla recommends keeping the battery charged. The battery performs better when it is plugged in all the time. Therefore, it is best to plug your Tesla in every night rather than only charging when the battery gets low. Not only will this help keep you from constantly worrying about how much energy your car has left, but it will also help your battery perform better and last longer.
This means if you are going to leave your car at home for weeks or days at a time, it is far better to leave it charging. Even when your car is not running it will lose some power, which means if you leave an electric car sitting for months it will eventually drain to zero.
It is not good for your car’s battery to hit zero! It is best to keep your battery above 30% capacity at all times, which means that it is best to have your car plugged in when you are not using it, especially for extended periods of time. Just make sure that you have the battery limit set to below 100% when doing this.
How Can I Make My Battery Last Longer?
All of this advice on best practices when charging a Tesla may make you wonder how you can make your battery last longer. As your battery degrades it will become less efficient in terms of energy storage and charging. What are some ways you can help your battery continue to operate at peak performance?
- Avoid extreme temperatures. Extreme cold and extreme heat are both bad for your battery. While you cannot exactly control the weather, being mindful can still make a huge difference. Park in the shade on hot sunny days, and if you can park in an enclosed area on extremely cold days.
- Do not fast charge all the time. Fast charging is wonderful because of its convenience, but your home charging system should be the main way you charge your Tesla. Charging at a Tesla Supercharger involves a much higher and faster transfer of energy, which causes your battery to heat more. Having your battery get hot regularly will cause it to degrade faster.
- Keep your battery capacity on moderate levels as much as possible. Driving around a lot on a low battery charge such as 15% will reduce the life of your battery, and driving around at 100% will decrease your car’s efficiency. Therefore it is best to spend most of your driving time in a middle range, between 30% and 80%, for the longest-lasting battery.
- Do not drive like your daily commute is a race. Teslas may have incredible performance in terms of speed and acceleration, but you do not need to push the level of what your Tesla can do. Not only is this dangerous, but also driving at consistently high speeds and with fast acceleration will wear down your battery.
Conclusion
To keep your Tesla charged and ready for use you should plan to charge it at home for several hours every day, typically overnight. There is no maximum as to the amount of time you should charge your Tesla, due to the ability to set percentage limits. Keep your Tesla with its battery between 30% and 90% for the best experience with these top-quality electric cars!